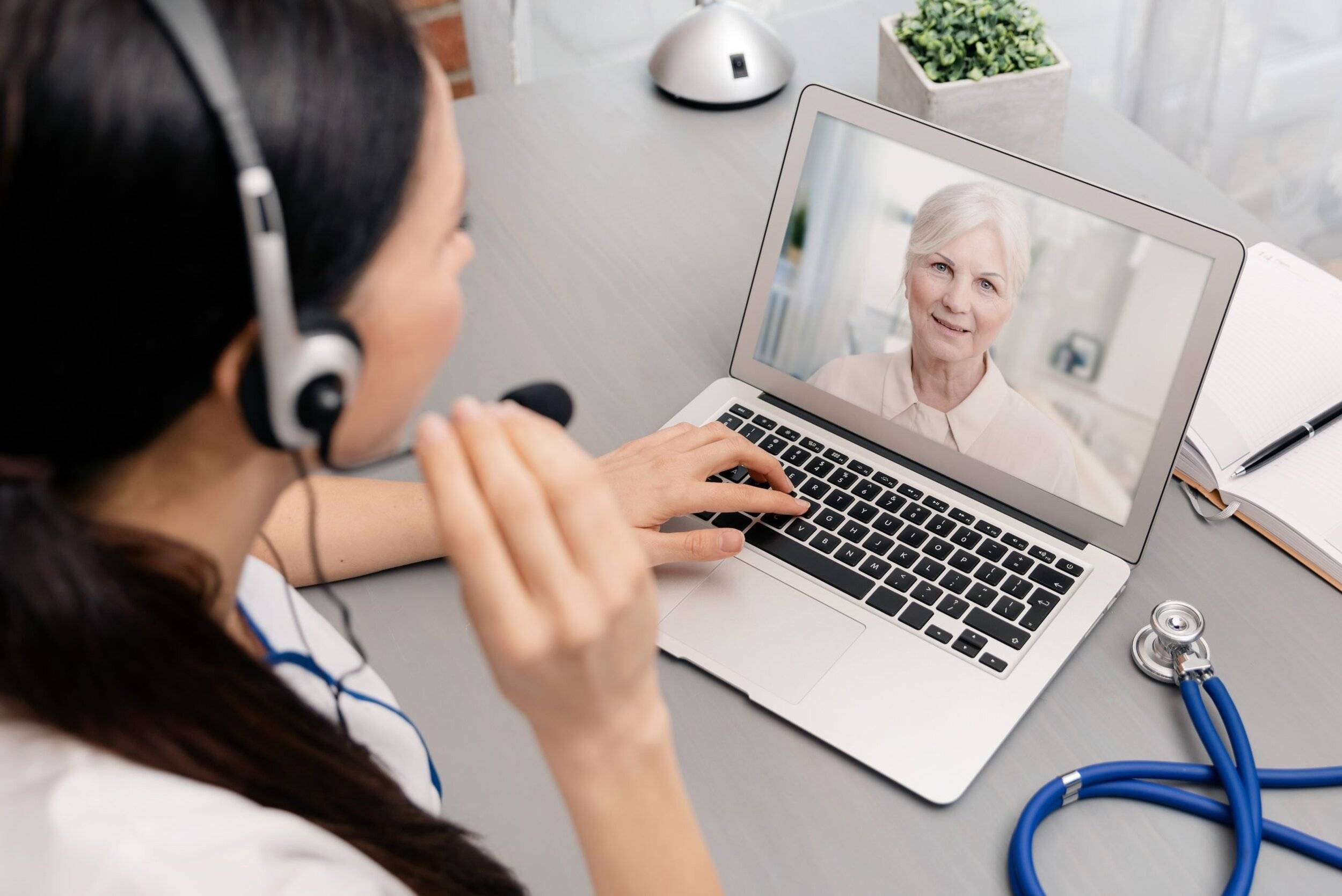
Imagine a future where you could see any remote specialist without ever leaving your house. Because of developments in telemedicine, this could soon become a reality. Telemedicine is the medical profession of providing clinical health care at a distance by utilizing telecommunications and information technologies. Patients can use telemedicine to connect with any specialist in the world via internet platforms.
Telemedicine is treating a patient without the doctor meeting the patient face to face by utilizing live pictures and sound and sending the patients their findings. The execution of telemedicine permits patients to get clinical consideration in a good way. Due to the Coronavirus pandemic, patients and professionals were obliged to adopt Telemedicine for health care services. Remote healthcare services are practical, cost-effective, and profitable, and they will become increasingly important in the future.
Although telemedicine and telehealth are optional, it is a good idea to become familiar with their distinctions and possibilities. Many people believe they are interchangeable. Both words refer to the provision of healthcare through the use of technology. Even yet, there is a distinction between the two.
The benefits extraordinarily offset any adverse consequences found in the present utilization of telemedicine. The most basic definition of telemedicine is delivering remote healthcare services via technology. Most sectors have already transitioned to remote (or on-demand) services when you think about it. Take, for example, banking. Walking down the street to a bank solely to deposit a check in a physical location seems outmoded, inconvenient, and unnecessary. The same might be said of waiting in a hospital lounge to see a doctor, which is famously problematic. Telemedicine technology is now available for use, with cloud-based, pay-per-use, and enterprise models all available. Aside from video conferencing, digital stethoscopes and other digital instruments and electronic medical records (EMRs) have all been tried and tested. The critical challenge in remote places is bandwidth availability and strength, as most solutions require adequate bandwidth for the upstream transfer of patient data.
Patients have already begun to receive online video consultations from healthcare specialists and facilities. Telemedicine has witnessed a significant increase in popularity, particularly since the commencement of the corona pandemic. Telehealth technology has advanced dramatically in the last decade, as has patient uptake. However, according to industry data, behavioral health (which saw a significant surge forward between 2012 and 2013) and specialty telemedicine services are driving the drive.
The shortfall of essential consideration specialists in rustic and detached places, alongside a maturing populace and many recently protected Americans under the Affordable Care Act, gives sufficient open doors for telemedicine to flourish. As per a recent report, the market for telemedicine innovation will increment at a build yearly development pace of 18.4% by 2020. Telemedicine is a means of using telecommunications and information technology to provide clinical healthcare to someone at a distance. Previously, telemedicine was only used to treat patients who lived in distant areas, far from medical facilities, or in areas where medical personnel were in short supply. The connected patient of today wants to spend less time in the waiting room at the doctor’s office and receive immediate care for minor but urgent conditions.
Telemedicine is helping to close the distance between patients and doctors that once existed. Patients not only feel more in control of their health exams, but doctors also have more time to analyze individual situations thanks to the help of outside physicians and specialists. A virtual office visit is the most typical telemedicine application. Patients will communicate alongside their doctors in real-time through a monitor, smartphone, or tablet, just like they would in the workplace. Patients will receive an introductory consultation, discuss preventive treatment and health, and review test results or scans, just as they would in a traditional office visit.
By creating area best practices and guidelines, wellbeing experts can expand the advantages of telehealth while holding the supplier patient coordinated effort, which is as yet the premise of excellent medical care.
The Future of Telemedicine in Healthcare
There are still many issues to work out regarding legality, security, ethics, and other vital factors. Still, as telemedicine advances, the impact and results can only be spectacular.
New technology is on the way, and augmented reality, biotech, virtual medical advancements, and wearables will be incorporated into this industry to provide more possibilities for providing care services, patient health monitoring, diagnosis, and treatment. The future of telemedicine isn’t just about expediting those operations; it’s also about putting systems in place to ensure that a patient’s inquiries aren’t just answered and also anticipated. That’s the real deal when it comes to digital health.
Telemedicine is inextricably tied to the overall innovation in the digital health industry. And what customers want from all healthcare services, not just telehealth, is to feel at rest, to be informed about their health, and to be able to communicate with their doctor if and when it’s essential. Attendant and doctor deficiencies will be eased by telemedicine. It’s critical to understand, however. However, it’s crucial to realize that Telemedicine’s advantages aren’t restricted to the expert domain; the patients we care about often have issues that can be tended to through telemedicine.
With the shortage of time among individuals, telemedicine has progressed significantly! Telemedicine offers a wide assortment of advantages alongside answers for all your medical problems with the simplicity of sitting at your place. Thus, telemedicine’s future is exceptionally bright and more requesting in the approaching time.
Assuming we go according to measurements of a study led on patients about the utilization of telemedicine, 74% of the reviewed patients would utilize telemedicine for counsel over their medical problems for anything going from gentle to medium.
Things/Apps like Skype, and Zoom, alongside present-day and skilled electronic contraptions, have displayed to individuals that counsel over video calls with a specialist is conceivable in the present time. In this way, individuals have likewise fostered interest and trust in telemedicine. Telemedicine doesn’t just end on video counsel through applications; as a matter of fact, the utilization of telemedicine has wide assortments. It relies upon how you utilize such an incredible subject. For example, in Jiyyo Innovations, Chandigarh makes awesome telemedicine in numerous ways.
Experts predict that telemedicine will no longer be considered a distinct form of medical practice. Medical care will combine delivery and consultation methods, ranging from 0% to 100% tele (at a distance), with all grades. As a result, it will become a meaningless term or label. In terms of penetration, it will grow gradually, barring ethical and legislative actions (such as those recently enacted in the American state of Texas). Still, it will not be the primary mode of medical practice, as many believe.
Many technologies are influencing the future of telemedicine trends in healthcare. The telemedicine market is growing as more people use smartphones and have access to high-speed internet. Wearable technology, telemedicine, genomics, virtual reality (VR), robotics, and artificial intelligence (AI) are among the new health technologies that are transforming the Indian healthcare sector.
Telemedicine has proven to be an effective way to improve patient access to medical care while also lowering healthcare expenditures. Patients in both rural and urban locations can now receive healthcare when they need it because of telemedicine. Nowadays, telemedicine can handle a wide range of tasks and is accessible to a far more considerable amount of patients. Because of the rapid development of smartphones, cellular connectivity and the Online have entered even areas where medicine is not always available. The ability to reduce the duration and material healthcare spending and diagnostic imaging became a key factor for the development of involvement in telehealth among doctors and medical institutions. Easy access to mobile solutions and their usability has increased the attractiveness of telemedicine for patients, and the ability to reduce the time and material costs of treatment and diagnostics became a critical factor in the growth of interest in telemedicine between many physicians and hospital organizations.
Given its relative underutilization compared to other telemedicine services like deliberational health and specialist telemedicine, recent findings imply that virtual chronic illness management provides a new market for telemedicine. These people require regular doctor visits, and using telemedicine to target this patient demographic could reduce the frequency of emergency room visits and hospital admissions. The “hospital at home” approach, in which patients who satisfy the requirements for hospitalization but are otherwise stable are treated at home for conditions such as chronic obstructive lung disease, pneumonia, and heart failure, is another expanding area in telemedicine.
Extensive research and technical breakthroughs will pave the way for a more in-depth look at emergency treatment and specialty medicine, such as teleophthalmology, OB-GYN, and mental health, in the future.
Telemedicine has several advantages.
- Improved medical resource allocation and fewer in-person visits result in cost savings and better efficiency.
- Reduced interaction with medical institutions minimizes the risk of infection. Patients can remain in their homes, lowering the danger of disease or other illnesses.
- Because the doctor’s availability has increased, patients can acquire their information sooner.
- Patients and doctors will have more flexibility as systems are modified to utilize the potential of telecommunications fully.
- A patient-centric strategy that prioritizes a positive User Experience.
- Access to healthcare practitioners in rural and distant places is improved.
- Patients with chronic ailments who cannot relocate from one location to another simply may appreciate the convenience.
Telemedicine is not appropriate for life-threatening situations such as a heart attack, cuts or lacerations, or broken bones that require x-rays, splints, or casts. Any problem that necessitates immediate, hands-on assistance should be handled in person. Telemedicine is also highly useful for simple queries and follow-up appointments.
If you suspect a cut is contaminated, you can schedule a virtual urgent care consultation with your healthcare practitioner to discuss your symptoms. If you’re on vacation and imagine you’re developing strep throat, go to your primary care physician. If you require birth control, you can discuss your requirements and receive a prescription the same day.
Colds and influenza, bug bites, sore throats, diarrhea, and pink eyes are all frequent illnesses that telemedicine is used to treat. Healthcare practitioners can also connect with patients via smartphone apps like Skype, Google Meet, and Zoom, as well as live video conference calls.
Telemedicine is a viable option for lowering readmission rates. One study by the New York Home Care Association looked at telehealth steps in five health care institutions for patients with heart failure, COPD, and pneumonia and found average readmission reductions ranging from 7% to 26%.
How Telemedicine changes the business of health care is that it brings patients and healthcare providers closer in a digital environment. Telemedicine is the use of technology that overcomes the gap between doctors and patients. Telemedicine is used for a diverse range of appointment types, including remote consultations and follow-up care.
Blackcoffer Insights 40: Krishna Vikas Thota and Shiva Lagishetty, Woxsen University