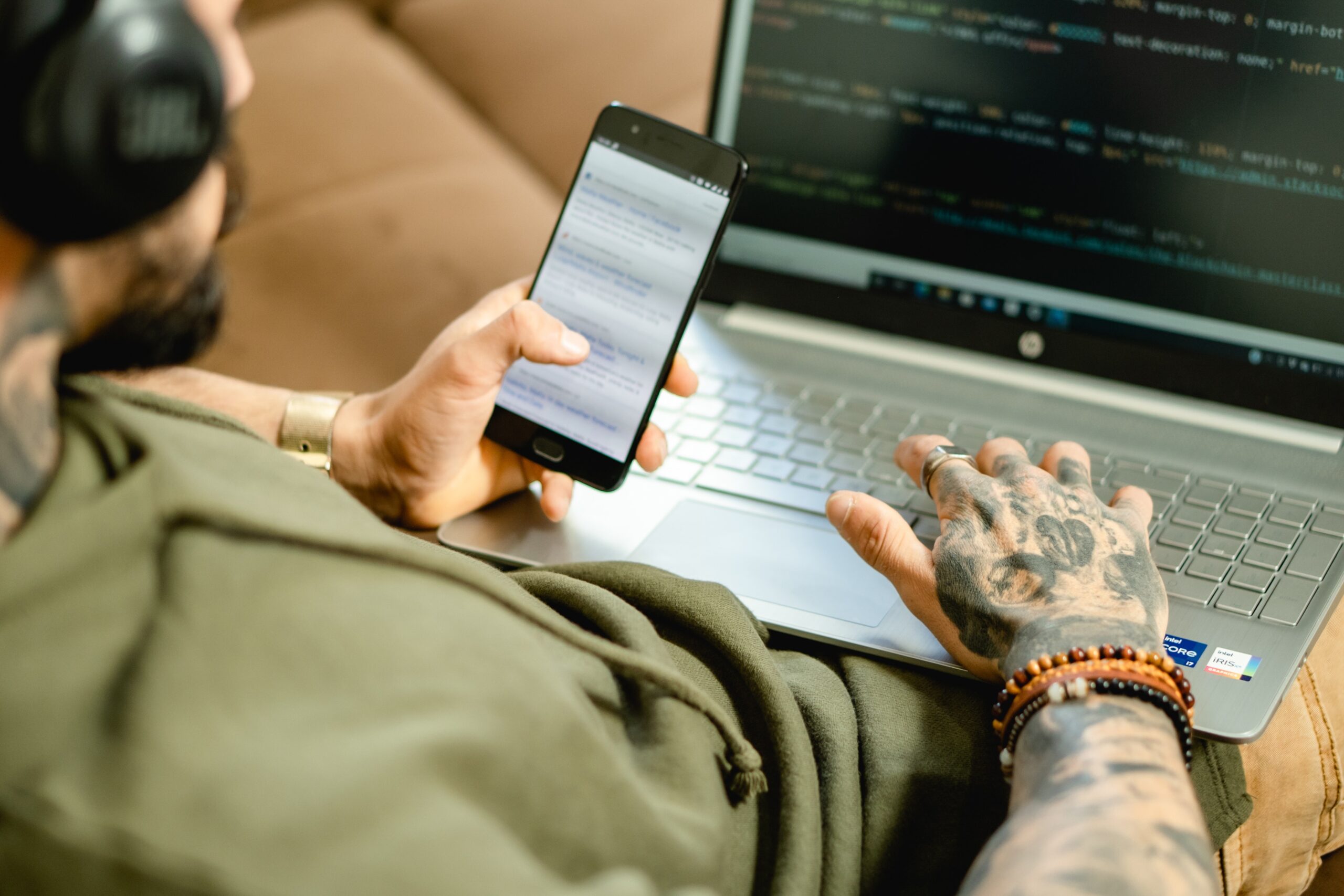
The way we live, work, and communicate has unquestionably changed as a result of the rapid evolution of technology. However, as we gain from digitization, we also leave ourselves vulnerable to cybercrime, a more sinister aspect of innovation. Cybercrime is a worrisome issue that has grown over time, and by the year 2040, its impacts are expected to be considerably more dangerous. This article examines the growing problem of cybercrime and its potentially wide-ranging effects, looking at how it may affect people, businesses, and even countries.
Cybercrime, which frequently involves illicit online behaviour, includes a variety of offences like hacking, identity theft, phishing, ransomware attacks, and more. The digital revolution of several industries, including finance, healthcare, and critical infrastructure, has unintentionally given cybercriminals a larger attack surface to find flaws and steal sensitive data. According to experts, cybercrime will have increased in frequency and sophistication by 2040. Cybercriminals will have additional opportunities to compromise networks and steal data as a result of cutting-edge technology like artificial intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Cyberattack complexity is predicted to reach previously unheard-of heights by 2040. The most robust defences will be breached by cybercriminals using cutting-edge technology like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and quantum computing. Attacks will be possible with greater accuracy, speed, and adaptability thanks to these advances. The impacts of cybercrime are felt throughout the entire world economy and go far beyond the digital sphere. The economic effects of cyberattacks may be devastating by 2040. Supply networks, financial systems, and critical infrastructure are all susceptible to breaches that might lead to generalised panic and financial instability. Because of this connection, domino effects and subsequent economic downturns are more likely to occur.
Impacts on the economy and financial disruption:
The economic effects of cybercrime are expected to be astonishing as its spread grows. Trillions of dollars in revenue could be lost as a result of the financial disruption brought on by cyberattacks on organisations and governments. By 2040, the interconnection of the world’s financial institutions will make it simpler for hackers to wreak economic havoc by crashing stock markets, banking networks, and supply chains.
Identity theft and invasion of personal privacy:
As hackers take advantage of people’s digital footprints, they will become more exposed to identity theft and breaches of their privacy. Identity theft is anticipated to become more sophisticated by 2040 when thieves can obtain personal data from numerous sources using AI and machine learning techniques.
Healthcare Sector’s Exposure:
Due to the sensitivity of patient data and the vital role it plays in society, the healthcare industry has emerged as a top target for hackers. By 2040, the integration of medical devices with digital systems may reveal weaknesses that would make it possible for cybercriminals to alter medical records, steal patient treatments, or even compromise personal health information.
Threats to national security:
Unprecedented threats to national security are posed by cyberattacks on vital infrastructure, including power grids, transportation networks, and communication networks. Such strikes might have disastrous effects by 2040, upsetting entire countries and unleashing an unprecedented level of turmoil. National security is no longer limited to conventional military threats in the digital age. The field of cyberwarfare will have grown greatly by 2040. Nations might become embroiled in cyber warfare, which might result in data manipulation, espionage, and even virtual sabotage. Cyberattacks have the potential to disrupt political landscapes, undermine defence systems, and impair military communication.
Disruption of Critical Infrastructure:
Cyberattacks on vital infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation networks, and healthcare institutions, may increase by the year 2040. Due to their interconnectedness with the internet, these systems are more vulnerable to prospective hacks, which might hurt entire societies. These assaults could jeopardise crucial services, healthcare, and public safety.
Surveillance and the erosion of privacy:
The degradation of individual privacy worsens as technology develops. By 2040, a complex network of interconnected gadgets may enable new levels of data collection and surveillance, raising questions about civil liberties and individual freedoms. Governments, businesses, and even cybercriminals could make use of this circumstance for a variety of reasons, including social engineering and extortion.
International Relations Restructuring:
Beyond national borders, the prevalence of cybercrime can alter global relations. States might interfere with elections, steal intellectual property, and engage in cyber espionage, all of which would exacerbate an already tense situation by sowing distrust and uncertainty. As countries struggle with concerns of cyber sovereignty and digital security, diplomacy may transcend beyond traditional channels and into the domain of cyber talks.
Interventions by the government and the law:
To prevent cybercriminals and hold them accountable, governments must implement strict laws and regulatory structures. Cyber rules that encourage responsible behaviour in cyberspace must be established through international collaboration and diplomatic efforts.
Developing Countermeasures:
The fight for digital security becomes more intense as criminality increases. The creation of countermeasures will be essential by 2040 for protecting sensitive data and crucial systems. Businesses and governments will make significant investments in cybersecurity research, AI-driven threat detection, and preventative defence systems. Robust cybersecurity frameworks will develop as a result of the merging of human expertise with machine learning.
Social Effects and Mental Health Costs:
The development of cybercrime is expected to have a significant social impact on people’s personal and psychological well-being. The ongoing risk of financial loss, data breaches, and digital manipulation may reduce public confidence in digital systems. Living in a constantly unstable digital environment can have a psychological toll that heightens stress, worry, and a lack of faith in technology’s promises.
Conclusion:
The development of cybercrime and its probable consequences by 2040 provides a gloomy perspective on the difficulties that lie ahead as we look into the future. While technological development has revolutionised our way of life, it has also ushered in a new period of criminal activities. Governments, corporations, and individuals must work together to combat these risks through thorough cybersecurity measures, global collaboration, and responsible technological development. We can work to guarantee a digital future that supports the principles of privacy, trust, and creativity by recognising the scope of the threat, investing in state-of-the-art defence systems, and encouraging a culture of cyber alertness. The battle against the shadowy side of the digital revolution is ongoing, as symbolised by the hashtags #SecureDigitalFuture and #CybercrimeBattle.
Blackcoffer Insights 47: Aseem Jain, Ajay Kumar Garg Engineering College, Ghaziabad (UP)