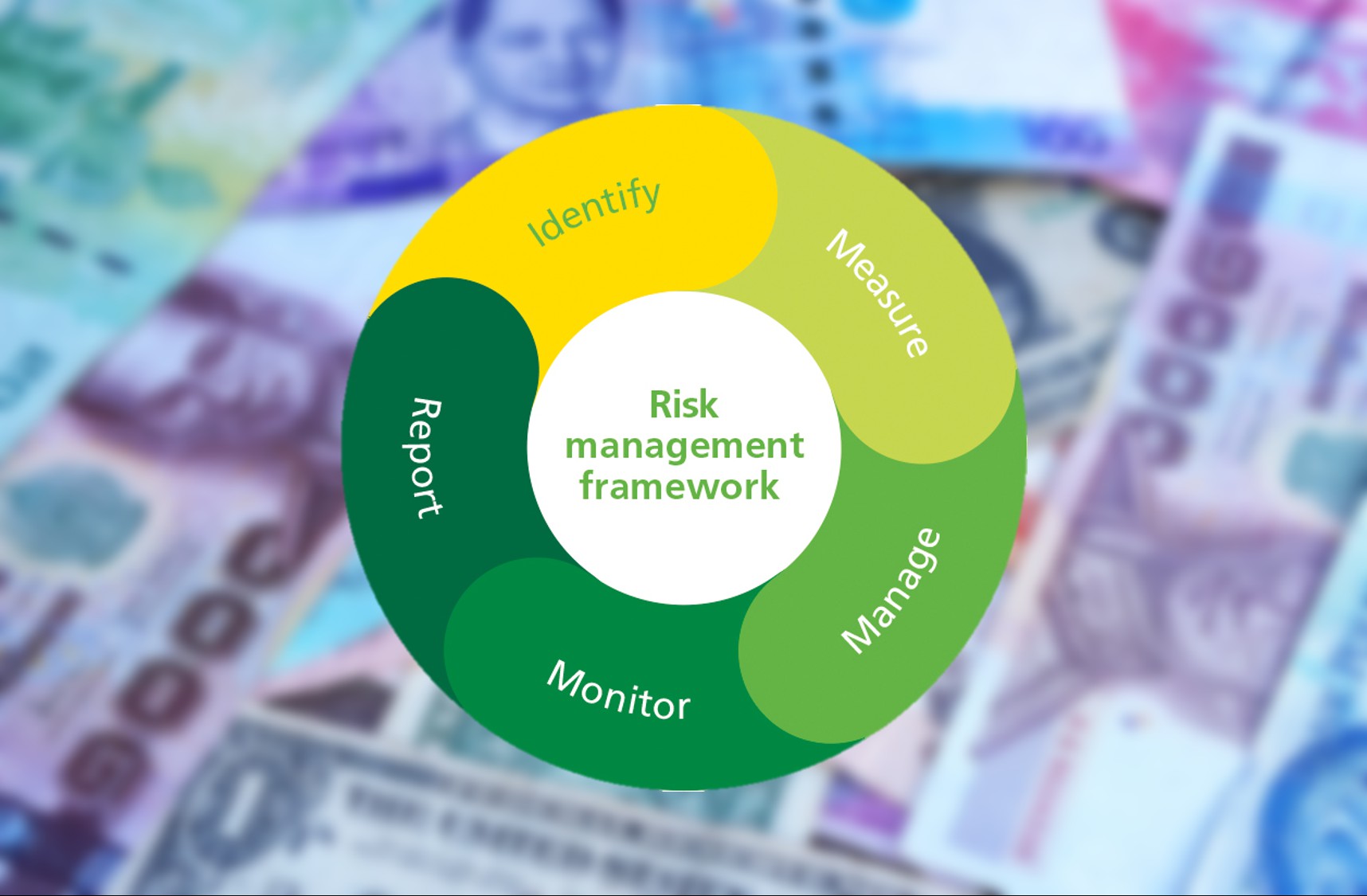
While buying shares or playing a betting game, we all might have used or heard the word…. RISK!!! Now, what does the word risk mean… it’s a fear of losing something of value, many times in monetary terms. The same saying goes for any financial institution. Bank operates in a dynamic business environment and faces multiple risks. With risk, comes the concept of risk management. Risk management refers to the identification and assessment of potential risk and the development and execution of plans to deal with such risks. In the banking industry, risk management focuses on managing the bank’s exposure to losses or risk and to protect the value of its assets, revenue, operations, business, and reputation.
To understand the future of Bank risk management, let us quickly go through the major banking risk one by one –
- Liquidity Risk – Risk when banks are not able to meet its short term financial obligations and day to day operational expense, leading to cash-crunch.
- Credit Risk – Risk of default of debt payment by the borrower attributes to credit risk. One can relate the credit risk with the 2007-08 financial crises were credit fell and the borrower was unable to pay their debts, which then turned into liquidity crises for the banks.
- Strategic Risk – Risk arising from the bank’s long term strategy. The bank needs to be agile to the needs of changing the business environment, or else it can lose market share.
- Compliance Risk – Risk arising from failure to comply with enforced laws and regulations. Reserve Bank of India fine on 19 banks including ICICI for failing to comply with its guidelines on the use of global payment network SWIFT is a good example of compliance risk.
- Cyber Security Risk –Phishing, malware, crypto-jacking, denial of service attack could affect the integrity and confidentiality of information.
- Reputational risk – Risk of loss of confidence of public Like Punjab National Bank, the second largest public sector bank in India, was defrauded for more than ~$1.8 billion by the largest diamond and jewelry businesses in the country, making it the largest fraud to be detected.
- Operation Risk – Faulty Internal process, systems, and human errors lead to operational risk.
Now how the future of the Bank Risk Management will look like –
- Process Automation – In the coming decade, most of the routine operational business process in risk dealing with customers will be automated. AI, algorithms, Machine learning will lead to increase in productivity and will help banks to reduce operational cost and chances of human error, thereby managing operational risk, compliance risk, and credit rate.
Some banks had already started investing in process automation. BNY Mellon’s, an American banking company, efforts to transition staff members to robotics and automation have resulted in huge sustained cost savings and increased productivity. As a result, there was better accuracy and faster processing, reducing transaction time and eliminating manual steps. Thus, resources redeployment created greater value for its clients. - Robust data infrastructure –There will be a need for reliable data pool at the back end and flexible infrastructure at the front end. This will make the customer more engaged with the bank through real-time data processing (like loan approval.) There will be huge investments in IT infrastructure, data centers, and software. A robust data infrastructure will be key to banking operation efficiency and risk minimization in the future.
TD Bank, a US national bank, has embarked on an effort to transform traditional banking data infrastructure into a more modern system built on a new application framework and APIs. - Collaborations – To meet the competition, many banks might collaborate with peer banks or Fintech startups to retain and gain a customer base and to manage third-party risk.
Fintech startups are the new buzz of the market, which provides highly competitive and seamless zero documentation services to customers, focusing on niche areas of the supply chain – origination, sales, and distribution. Bank can collaborate with these fin-tech companies or peer banks in effectively managing third-party risk.
Banks like Citizens bank, Ally bank have joined together as investors and members in KY3P a company dedicated to working with the financial industry to standardize best practices for managing third-party risk and optimizing the processes by which financial institutions assess and monitor inherent risk in engaging suppliers and entering into third-party relationships. - Analytics and Machine learning – It is a tool which will be widely used by the financial institutions especially where data needs to be interpreted and acted upon. It will help banks to manage risk-appetite, by providing meaningful data patterns and trends, which will form the base for decision making-Like Improvement in the identification of risky customers (considering default risk). From top to bottom, machine learning will be integrated into the process and will become an integral part of the overall process.
PayPal is one of the best examples – The company, which supports 7.8 billion payment transactions annually in more than 200 countries around the world, is deploying technology thereby enabling the usage of data-driven intelligence across the entire value chain. - Manpower Talent Pool – In the coming future, there will be a shift of resources allocation from processes to data analytics. At present, almost 50% of staff is handling operational process which will be bought down to 15-20% and Analytics will employ 40% of manpower (which is 15% at present) Bank will hire a lot of different talent pool who understand application of data analytics and statistics in decision making. Banks will partner with top universities and institutes (featuring training in data analytics) as a part of risk management. Apart from hiring, retaining talent and continuous knowledge upgrade will also become a focus area for banks.
- System Audits – Since many operations will be automated, system audits will play a very crucial role to ensure reliability and efficiency of data systems. System audit will play a crucial role in identifying loopholes in the systems and thus, bringing out areas of the potential risk so that timely corrective action plans can be put in place to mitigate risk. Auditing in the future will focus on creating risk-based audit plans and testing the frameworks, rather than just controls.
- Cyber Security – Mobile and internet penetration has rocketed the use of internet banking. Increasing the risk of leakage of confidential information can put operations of the bank to halt. The average cost of cybercrime for financial services has increased from $12.97 million USD per firm in 2014 to $18.28 million USD in 2017, which is almost 40 percent over the past three years. To minimize cyber risk, the bank will make major investments in cybersecurity. Minimize cybersecurity threat in the future will be one of the most challenging tasks in the future, considering its nature and huge risk potential attached to it.
Banking risk management will undergo a major change from what it looks now, as there will be new challenges for the business. Customers want real-time service and update, which will require huge investments in technology and Artificial intelligence. There would be pressure on banks to provide real-time services with a reduced cost (affecting bank margins). With the financial crises day on day, new regulatory norms are introduced, maintaining a strict check on liquidity and capital adequacy. The bank needs to invest in proper IT infrastructure which is not only reliable but also flexible. Upcoming Fintech startups will also add on to the strategic risk of the banks. Not to forget the Cyber risk which will become one of the top risks for banks in the coming decade.
To cope with the above risks, banks need to put more robust and reliable risk management in place. By the end of this decade, or even earlier, the active approach of the financial institutions in handling the risk functions will determine its success or failure. They need a have proactive approach in identifying, assessing and mitigating risk through better IT infrastructure, machine intelligence, better resources allocation/mapping, real-time analytics, and internal control frameworks. However, one can bet that the future will belong to those who will have a go-ahead approach in identifying, assessing and putting effective risk minimization plan to actions.
Blackcoffer Insights 9.0, Monica Jain, IIM, Indore