Will COVID19 END Globalization?
Globalization:
Globalization envisages a borderless world or seeks the world as a global village • It is attributed to the accelerated flow of goods, people, capital, information, and energy across borders, often enabled by technological developments.
Globalization Trends:
Starting from 1990s globalization dominated world’s economic order.
Anti-Globalization Wave:
Globalization had already begun to stagnate since the 2008-09 Global Financial Crisis.
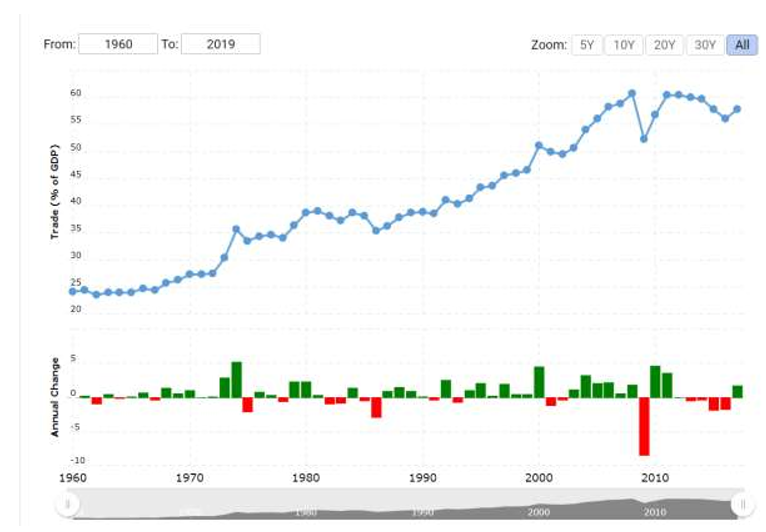
Slowing Down of Trade:
Trade as a percentage of global GDP increased from 39% in 1991 to 61% in 2008 but has stagnated over the past decade.
Countries Policies Reflecting the Reverse Globalization:
The following polices and steps of various countries shows the protactinium
1.USA
We reject Globalism, President trump took ‘American First to the United States – Trump
2. Brexit
Brexit is a rejection of globalization-Larry Elliott
Slowing Movement of People:
Though number of tourists increased in the last decade.
1.Indian IT’s H-1B Visa woes could worsen in 2020
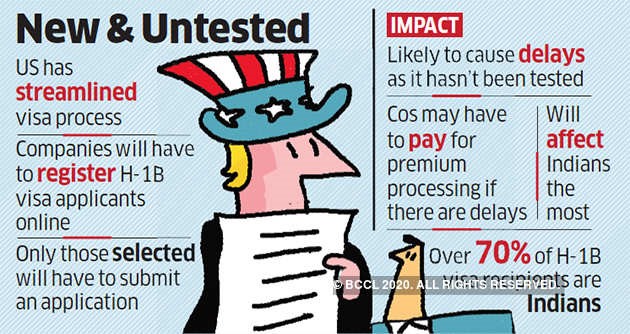
The above article reveals that Under the Trump administration, Indian IT services companies have seen rejection rates jump from 6% in 2015 to 24% in 2019.
2.Racism study finds one in three school students are victims of discrimination
Trade Wars and Halting of WTO Talks: Retreat of Globalization:
1.Chinese-US trade war threatens globalization
2.Protectionists put brakes on trade liberalization
Due to These Factors, International Media Is Referring to The Process of Globalization By The Term ‘SLOWBALISATION’
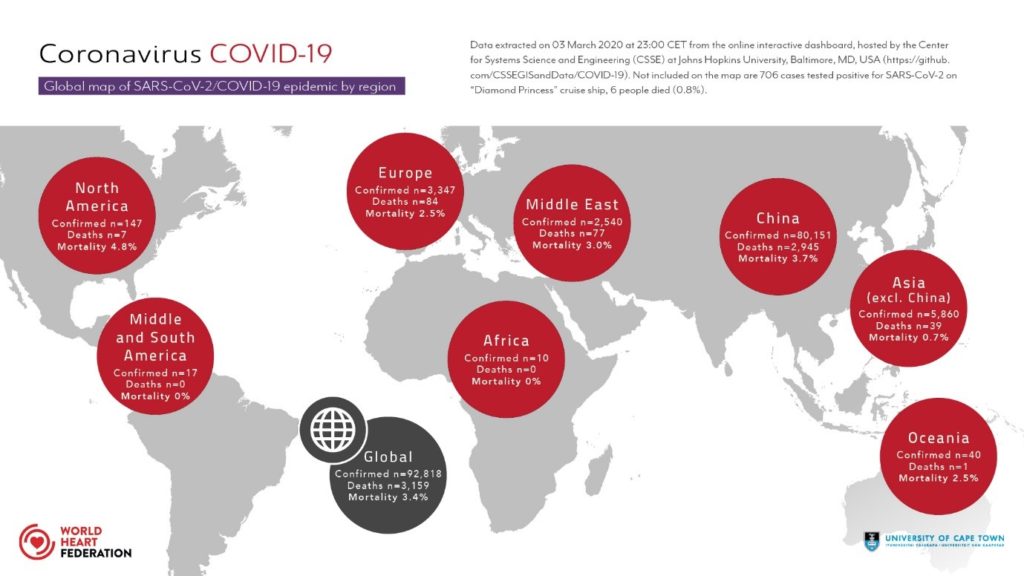
The ongoing phase of globalization has not fully recovered, and the recent coronavirus has pushed forward the trends of reverse globalization
Globalization Is Responsible for The Spread Of Coronavirus:
- The virus started in Wuhan, China
- China, being a hub of many industries. People from all over the world are travelling in and out of China
- Italy itself a tourist and business hub, the man in Delhi who tested positive for coronavirus had travelled to Italy
- Other countries get the virus because of the movement of people and goods
Corona Virus Has Halted The Movement Of People, Goods, Service, And Capital.
More than a fifth of the world’s population has been under lockdown in the global fight against coronavirus with early sign of success.
Due to Supply Chain Break Down In China because of Coronavirus
Countries Providing Incentives To Shift Production To Their Native Country
Amid Covid-19 World Trade Has Halted, Investors Are Pulling Out Money from The Market
Other Side Of The Coin!!
Corona Virus Won’t End Globalization, But Change It Hugely for The A Better
- Will Hutton
An unregulated world can be blamed for its spread, but collective action based on evidence could be the best way to stop it.
Trade During Coronavirus:
1.India Readies list of 13 countries to send hydroxychloroquine.
2.China Sends doctors and masks overseas domestic coronavirus infection drop.
Movement of Ideas
Countries are converging virtually to share best practice to fight pandemic
International meeting such as G-20, SAARC summit organized virtually
Living apart, we must stand together’ to battle coronavirus pandemic-UN Rights chief.
China’s BRI Project after COVID-19
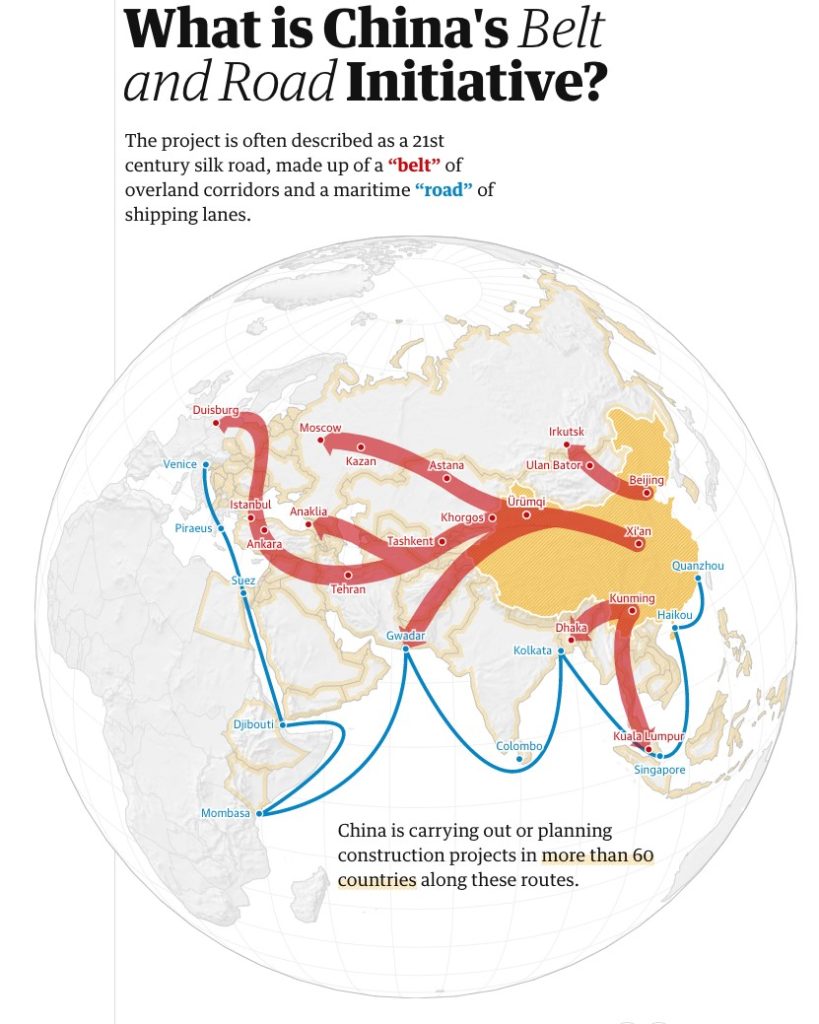
BRI Project:
The Belt and Road Initiative is a global development strategy adopted by the Chinese government in 2013 involving infrastructure development and investments in nearly 70 countries and international organizations in Asia, Europe, and Africa.
Curtailed Connectivity after Covid19:
A devastating economic collapse of potentially historic proportions after Covid19, leading to social and political turmoil in a number of countries, and curtailed connectivity. Interestingly, the pandemic has exposed the risks and weaknesses of global interconnectedness, which will affect China’s BRI.
Funding Shortfall for BRI
So far, BRI has been powered primarily by China, whose growth rates were decreasing even before the outbreak. Exports Hit: With the United States and Europe reeling from the pandemic, Chinese exports will take a big hit.
China confronts major Risk of debt on belt and road due to pandemic
China’s growth hit a near 30-year low of 6.1%
Roughly 5 Million people in china lost their jobs in the first 2 months of 2020.
Last February, China’s official urban unemployment jumped to an unprecedented 6.2 percent. Unemployed Number may go up to 9 million by the end of 2020.
China will have to choose out of two competing priorities:
- avoiding the middle-income trap,
- while at the same time posturing as a superpower abroad.
So, not only may BRI be short of cash, but it will also be hard to sell at home
All Economies along BRI routes affected
Pakistan, host to the biggest BRI megaproject in the world, is poised to sustain a $8.2 billion loss, according to ADB. The respective figure for Bangladesh is $3 billion. Thailand is now bracing up for a recession. Africa is equally vulnerable, as China is the continent’s largest market.
Covid19 hit Chinese companies executing BRI contracts can rely on support from the CDB in the form of low-cost financing. Yet, Chinese policy banks will be increasingly picky and inclined to stay away from new projects that may turn out to be loss-makers.
China Development Bank to support Belt and road companies hit by coronavirus -Xinhua
The Coronavirus and Xi Jinping’s Worldview
Priority list:
No. 1 preserving the CCP’s power
No. 2 maintaining national unity
No. 3 the expansion of the economy No. 4 environmental sustainability
No. 5 modernize the Chinese military
No. 6 China’s 14 neighboring states
No. 7 weaken America’s longstanding security alliances No. 8 terrestrial Silk Road Economic Belt No. 9 Maritime Silk Road
No 10 reshape the global order
Under extreme circumstances, Beijing will not consider the BRI as important.
Is the BRI Finished then? Short Term: Yes, BRI will Face Trouble
In particular, the summer of 2020 may be a period of hibernation for several BRI projects.
The outbreak has brought Chinese labor supplies and equipment imports along BRI routes down to a trickle
Not Exactly!!! In fact, the initiative’s fuzzy content is being further enriched with the “Health Silk Road” add-on narrative and “mask diplomacy” in a major soft-power push.
Long Term: A Changed BRI will Emerge
The BRI is bound to change. Strategies will change.
It might even be Defined Properly
Seven years after this ambitious initiative was announced it remains a blurred vision in need of a comprehensive conceptual framework, international standards, and a coherent implementation strategy.
This is one of the reasons why the BRI has become controversial and has caused a backlash in many countries.
A Shift away from Roads and Bridges
BRI expenditure up to 2019 stood at $545 billion. (WB Estimate) About two-thirds of spending on BRI projects has gone into the energy sector and transport
However, developing countries in need of infrastructure will be terribly cash-strapped, there may be a shift away from roads, bridges, and coalfired power plants funded through Chinese loans.
New BRI projects will probably be more strategically chosen.
Beijing has been investing in the creation of a globe-spanning network of economic corridors, logistics zones, and financial centers, with stress laid on seaports and adjacent areas. Egypt’s Suez Canal Economic Zone and Sri Lanka’s Colombo Port City clearly show this trend.
In addition, projects are likely to focus on more sophisticated forms of connectivity, such as 5G networks or, in the wake of the pandemic, disaster management, public health-related high-tech, and even remote surgery. China will surely use the BRI for the projection of its soft power, an increasingly important battlefield in international relations.
The world has become aware of the risks of overwhelming reliance on China.
Amid of Coronavirus outbreak we can see the major economies are strengthening their authorities with their major concern
- The USA is conducting space mining
- China’s maritime Aggression
- India USA $155 Million Defense Deal, US Approves sale of Anti-Ship Missiles and torpedoes to India.
Blackcoffer Insights 17: V.Jagan, IIM Kashipur